God, grant me the serenity to accept the things I cannot change, The courage to change the things I can, And the wisdom to know the difference. (Serenity Prayer, Reinhold Niebuhr)
Transportation
Transport or transportation is the movement of humans, animals and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles and operations. Transport is important because it enables trade between people, which is essential for the development of civilizations (Wikipedia).
Transport infrastructure consists of the fixed installations, including roads, railways, airways, waterways, canals and pipelines and terminals such as airports, railway stations, bus stations, warehouses, trucking terminals, refueling depots (including fueling docks and fuel stations) and seaports. Terminals may be used both for interchange of passengers and cargo and for maintenance (Wikipedia).
Modes of Transportation
Mode of transport is a term used to distinguish substantially different means of conveyance. The different modes of transport are air, water, and land transport, which includes rail, road and off-road transport. Other modes also exist, including pipelines, cable transport, and space transport (Wikipedia).
- Rail - (12% of total) handles the largest ton-miles in the US. Has high fixed and low variable costs.
- Highway - (68.9% of total) - largest share of transportation. Has low fixed and high variable costs. Effective for small shipments moving shorter distances. Truckload (TL) is a full truckload being hauled. Less-Than-Truckload (LTL) is less than a full truckload
- Water - (7.7% of total) - includes the Great Lakes, canals, and intracoastal waterways. There has been a shift in bulk transportation from rail and highway to water. Water has the capacity to move extremely large shipments. Ranks between rail and truck in fixed cost. Water is slow and has limited range of operation.
- Pipeline - (9.4% of total) - highest fixed cost and lowest variable cost. Coal slurry pipelines are a new trend but require a lot of water.
- Air - (0.1% of total) - speed, but high cost, especially as weight increases. Low fixed cost and high variable cost. There have been the development of all freight airports so it doesn't interfere with passenger traffic.
Mixed Modes
- Multimodal solutions are transportation solutions that seek to exploit the strengths of multiple transportation modes through physical, information and monetary flows that are as seamless as possible.
- Roadrailers are specialized rail cars the size of standard truck trailers that can be quickly switched from rail to ground transport by changing the wheels.
Types of Carriers
Common carriers are also known as public carriers; transportation service providers who handle shipments on a case-by-case basis, without the need for long-term agreements or contracts.
Contract carriers are transportation service providers who handle shipments for other firms based on long-term agreements or contracts.
Third-party logistics providers are service firms that handle all of the logistics requirements for other companies.
Freight forwarder is an agent who serves as an intermediary between the organization shipping the product and the actual carrier, typically on international shipments.
Custom’s broker is an agent who handles customs requirements on behalf of another firm. In the United States, customer brokers must be licensed by the Customs Services.
Measuring Logistics Performance
A “perfect order” is a term used to refer to the timely, error-free provision of a product or service in good condition.
Performance can be measured as the percentage of orders that meet the “perfect order” criteria.
Percent of perfect orders = (total orders – orders with >1 defect) / total orders
US Trade & Transportation
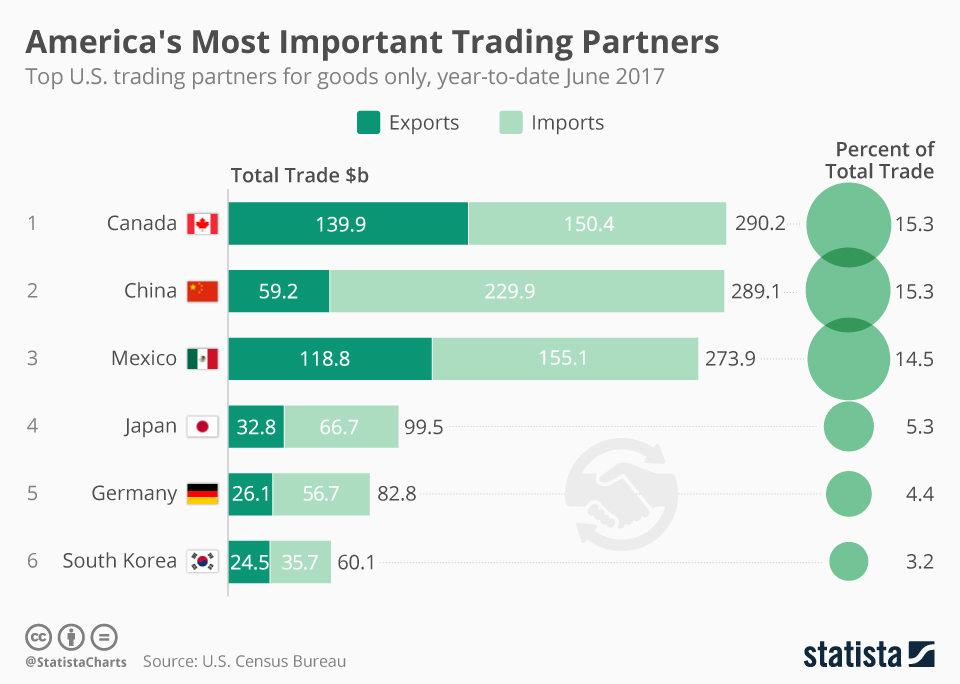
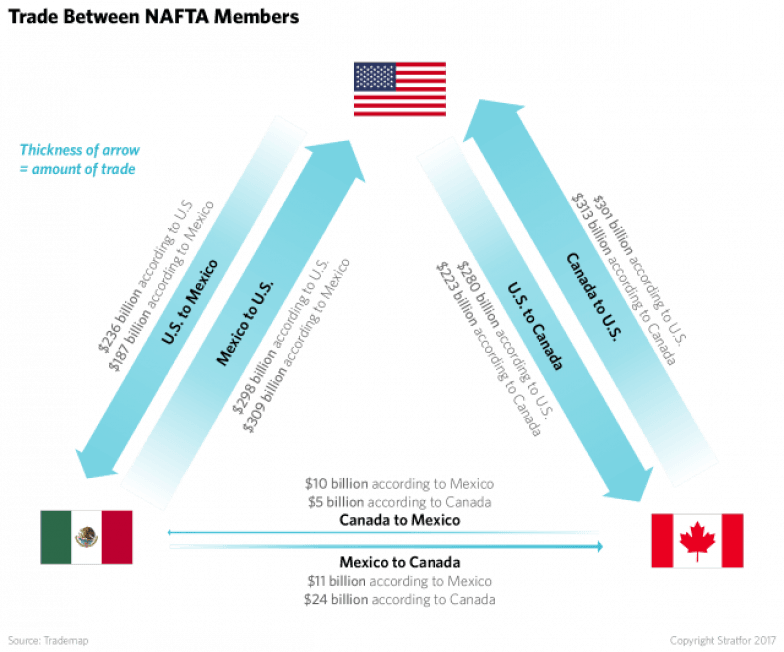

Transportation Service
- Ground Package Service - USPS, FedEx, UPS
- Intermodal Transportation - piggyback service - integrated rail and motor service.
- Trailer on a Flatcar (TOFC)
- Container on a Flatcar (COFC)
- Containerships - One 15-ton barge has capacity of 225 railcars or 900 trucks
Transportation Economics
Economic Factors
Economies of scale in transportation - the cost per unit of weight decreases as the size of a shipment increases. This is due to the use of larger capacity vehicles (rail/water) and the allocation of fixed costs over a larger base. Economy of distance - the cost per unit of weight decreases as distance increases. Also due to spreading the fixed costs across more weight miles (also known as the tapering principal).
- Distance - cost curve increases at a decreasing rate with distance (tapering principle)
- Weight - cost per unit of weight decreases as load size increases
- Density - higher density products are cheaper per unit of weight
- Stowability - how product dimensions fit into transport equipment
- Handling - special handling equipment increases cost if required
- Liability - risk of damage in transport (function of packing/type)
- Market - amount of shipment along the transportation lane that makes the market more or less costly to serve.
Transportation Rates & Ratings
Transportation Participants
- The shipper / the consignor
- The destination / the consignee
- Carriers and agents - uses shipment consolidation and coordinated pickup & delivery times to reduce cost to increase profit. Brokers and freight forwarders facilitate carrier and customer matching.
- Government
- Internet - marketplace for carriers, and matching freight capacity
- The public - wants a safe, environmentally responsible system
Regulation
Economic Regulation
Economic regulation controlled entry, rates and services, treating each type of transportation independently. The degree of US government control over economic regulation was reduced significantly during the 1980's.'
Social Regulation
- The Federal Department of Transportation (DOT) controls the transport and handling of hazardous material and rules related to driver hours and safety. The Transportation Safety Act of 1974 formally established safety and social regulation.
- The Hazardous Material Transportation Uniform Safety Act of 1990 established control over equipment design, hazardous material classification, packaging, and handling.
- The Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) was formed in 1887. The ICC rules that shipments from warehouses to markets in the same state could be deemed interstate movement if the commodity had originally been shipped from out of state.
- The Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act of 2000 gave electronic documents signed by digital signature the same legal status as paper documents.
- The US Department of Defense (DoD) mandated that its suppliers attach Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags to any goods sold to the military.
- The Jones Act mandates that only US built ships operating under a US flag and with a US crew can ship goods directly from a US port to another US port.



